Here you will find answers to the following questions:
|
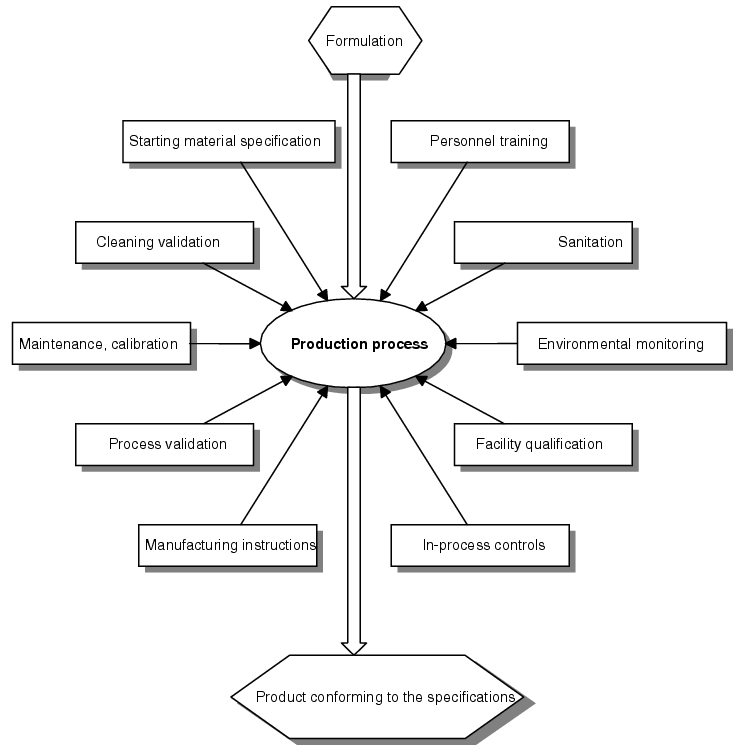
The manufacturing of specification-compliant products depends on the existence of various quality assurance elements. The quality of the individual elements determines the probability with which manufacturing will be carried out without problems, i.e. within the prescribed limits. Reproducible production is only feasible given these limits and their mutual interaction. It is the task of the quality assurance system to guarantee this constellation (see figure 11.F-1).
Ideally, quality control of the final product would not be necessary if correct manufacturing could be guaranteed by the environment. However, due to the many different influencing factors, this only applies in theory. Furthermore, the legislator prescribes final product quality control for pharmaceutical products. The care with which the surrounding and preliminary influencing factors are managed is responsible for the effort that must be made in the actual production.
In addition to the elements listed, the aspects shown in figure 11.F-2 also represent important values for GMP-compliant production.
| GMP aspects in the production process |
|---|
|
Self-inspections are an important way of guaranteeing the GMP status within the plant, in this case production. These inspections help uncover deficiencies and highlight possibilities for optimisation. A permanent TARGET/ACTUAL comparison of requirements of the quality assurance system and its practical implementation helps improve the status. The inspections should be considered as an opportunity to promote the GMP-specific development process. (See chapter 18.E Self-inspection.)
Summary Different quality assurance elements help create a GMP environment in which specification-compliant products can be manufactured. In addition to the GMP-compliant environment (rooms and facilities), this also includes controlled processes, trained staff and a dense network of instructions and records. |